Here are some science questions to help you test your general science knowledge. They will also show you which of the Florida, Utah, and NGSS science standards each question is testing.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
Get 5 more random questions.
Would you rather see the most recently added questions?
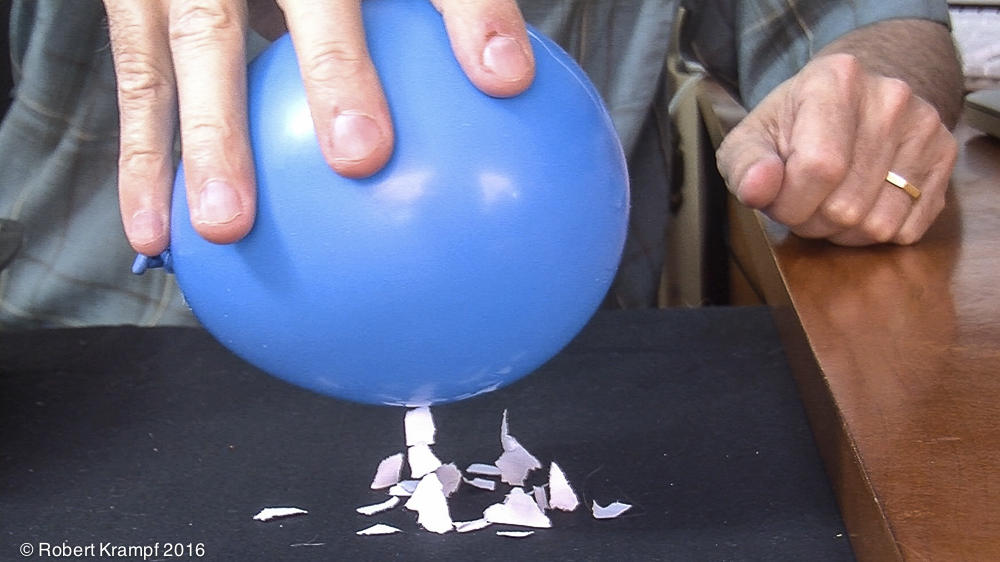

I gave this balloon a negative electrostatic charge by rubbing it on my hair. Then I tore up bits of paper, and put them on the table. When I brought the balloon near them, they were attracted to the balloon. Why?
-
The negative charge of the balloon induced a positive charge on the paper.
Yes! The negative charge on the balloon pushes some of the negatively charged electrons in the paper to the far side, leaving the near side with a positive charge. Opposite charges attract, so the paper is attracted to the balloon. -
The negative charge of the balloon attracts the neutrally charged paper.
No. As long as the paper is neutral, it will not be attracted or repelled. -
Tearing the paper gave it a positive charge.
No. If the paper had a positive charge from being torn, the bits of paper with like charges would have repelled each other before you moved the balloon nearby. -
Paper is always attracted to balloons.
No. This is easily tested by using a balloon that has not been rubbed on your hair. Without the positive charge, the paper is not attracted.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.P.10.3 Investigate and explain that an electrically-charged object can attract an uncharged object and can either attract or repel another charged object without any contact between the objects.
>>> Teacher Page: Electrostatic Charges
| Electrostatics and Water | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Challenge: Paper, Coin, Cup, part 2 | video |
| Sorting Salt and Pepper | video, checked |
| Electricity | video, free, Updated |
| Making Water Wiggle | video |
| Challenge: Paper, Coin, Cup, part 1 | video |
| Electrostatic Charges | video |
| The Leyden Jar | video, checked |
| Versorium | video, checked |
| Review Energy-6 | quest |
| Review Energy-7 | quest |
| Review Energy-8 | quest |
SC.6.P.13.1 Investigate and describe types of forces including contact forces and forces acting at a distance, such as electrical, magnetic, and gravitational.
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Challenge: Paper, Coin, Cup, part 2 | video |
| Light a Bulb with a Balloon | video, checked |
| Crushed Can | video, checked |
| Electricity | video, free, Updated |
| The Compass and Magnetic Fields | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Challenge: Paper, Coin, Cup, part 1 | video |
| Making a Compass | video, checked |
| Torque | video |
| Versorium | video, checked |
| Review Energy-6 | quest |
| Review Energy-7 | quest |
| Review Energy-8 | quest |
Utah
UT.5.IV.1.c Describe the behavior of objects charged with static electricity in attracting or repelling without touching.
| Electrostatics and Water | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Challenge: Paper, Coin, Cup, part 2 | video |
| Sorting Salt and Pepper | video, checked |
| Making Water Wiggle | video |
| Challenge: Paper, Coin, Cup, part 1 | video |
| Electrostatic Charges | video |
| The Leyden Jar | video, checked |
| Versorium | video, checked |
| Review Energy-6 | quest |
| Review Energy-7 | quest |
NGSS
MS-PS3-2 Develop a model to describe that when the arrangement of objects interacting at a distance changes, different amounts of potential energy are stored in the system.
| Versorium | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Electrostatics and Water | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Challenge: Paper, Coin, Cup, part 2 | video |
| Sorting Salt and Pepper | video, checked |
| Making Water Wiggle | video |
| Measuring Kinetic and Potential Energy | video, checked |
| Challenge: Paper, Coin, Cup, part 1 | video |
| The Leyden Jar | video, checked |
| Review Energy-6 | quest |
| Review Energy-7 | quest |
| Review Energy-8 | quest |
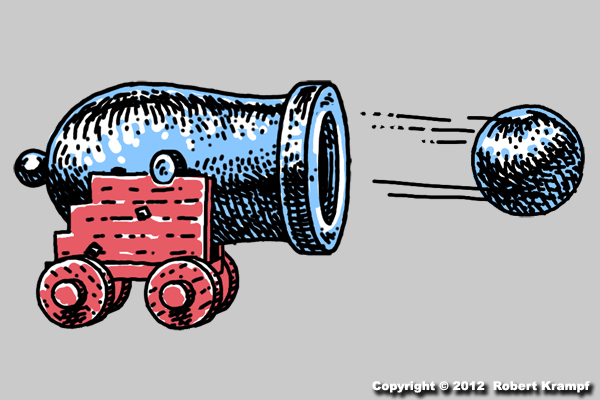
When this cannon fires, cannon and the cannon ball both move, but the cannon ball moves much farther and faster than the cannon. Why?
-
The cannon ball is smaller.
No. While smaller size means a little less air resistance, that is not enough to cause the difference. -
The wheels on the cannon are stuck.
No. Even with the wheels moving freely, the cannon ball will still move much faster and much farther. -
The cannon ball is round.
No. While the round shape means a little less air resistance, that is not enough to cause the difference. -
The cannon ball weighs less.
Yes! According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, the more mass an object has, the less it will be affected by a force. Newton's Third Law of Motion tells us that the cannon and the cannon ball will both be pushed by the same amount of force, but since the cannon is much heavier (more mass), it will not move as fast or as far.If the cannon was made of very light weight plastic, so that it was much ligher (less mass) than the cannon ball, then the cannon would move farther and faster.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.P.13.3 Investigate and describe that the more mass an object has, the less effect a given force will have on the object's motion.
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| High Bounce | video, checked |
| The Difference Between Weight and Mass | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
Utah
UT.3.III.2.b Compare and chart the relative effects of a force of the same strength on objects of different weight (e.g., the breeze from a fan will move a piece of paper but may not move a piece of cardboard).
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| High Bounce | video, checked |
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
NGSS
MS-PS2-2 Plan an investigation to provide evidence that the change in an object’s motion depends on the sum of the forces on the object and the mass of the object.
| Torque | video |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Newton's First Law of Motion | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 2 | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 1 | video, checked |
| Science Friction | video, checked |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| More Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Science of Balance | video, checked |
| The Old Tablecloth Trick | video |
| Bernoulli Effect | video |
| Smoke Rings | video |
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| The Difference Between Weight and Mass | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |
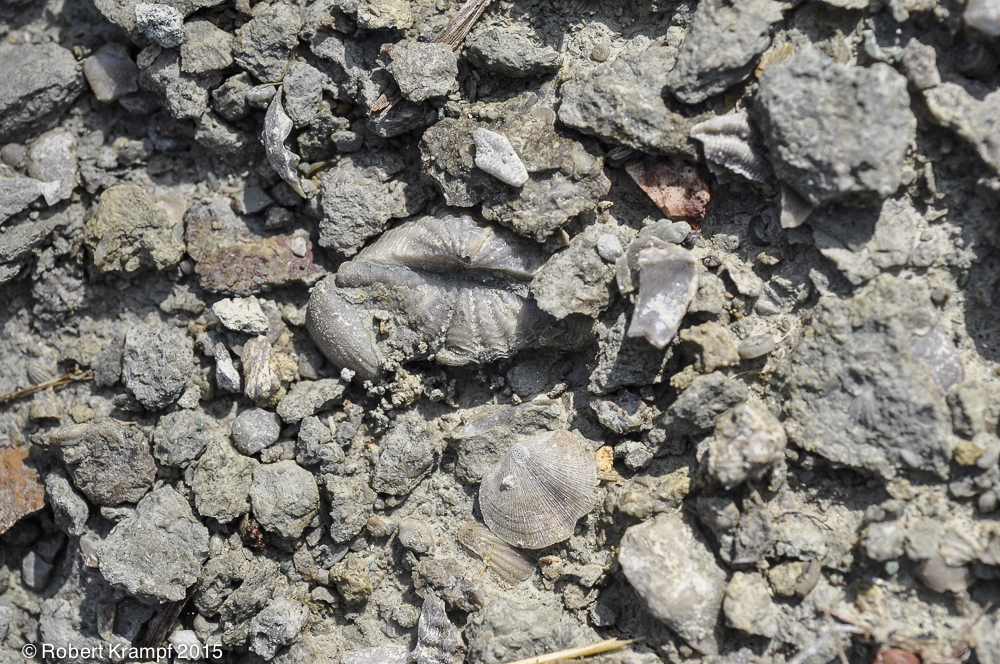

This limestone is in Middle Tennessee, and contains a wide variety of fossils of ocean creatures. What kind of rock is limestone?
-
Igneous
No. Igneous rocks are formed from molten lava or magma. -
Sedimentary
Yes! Sedimentary rocks are made up of bits of other rocks that have been deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity. This limestone was deposited by the ocean, making it a sedimentary rock. -
Metamorphic
No. Metamorphic rocks have been changed by heat and/or pressure. If this limestone was exposed to tremendous heat and pressure, it could change into a metamorphic rock called marble. -
Limestone is not a rock.
No. Limestone is a naturally occurring solid that forms large layers in the Earth. It is a rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.d Classify common rocks found in Utah as sedimentary (i.e., sandstone, conglomerate, shale), igneous (i.e., basalt, granite, obsidian, pumice) and metamorphic (i.e., marble, gneiss, schist).
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
UT.8.III.1.c Categorize rock samples as sedimentary, metamorphic, or igneous.
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
NGSS
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
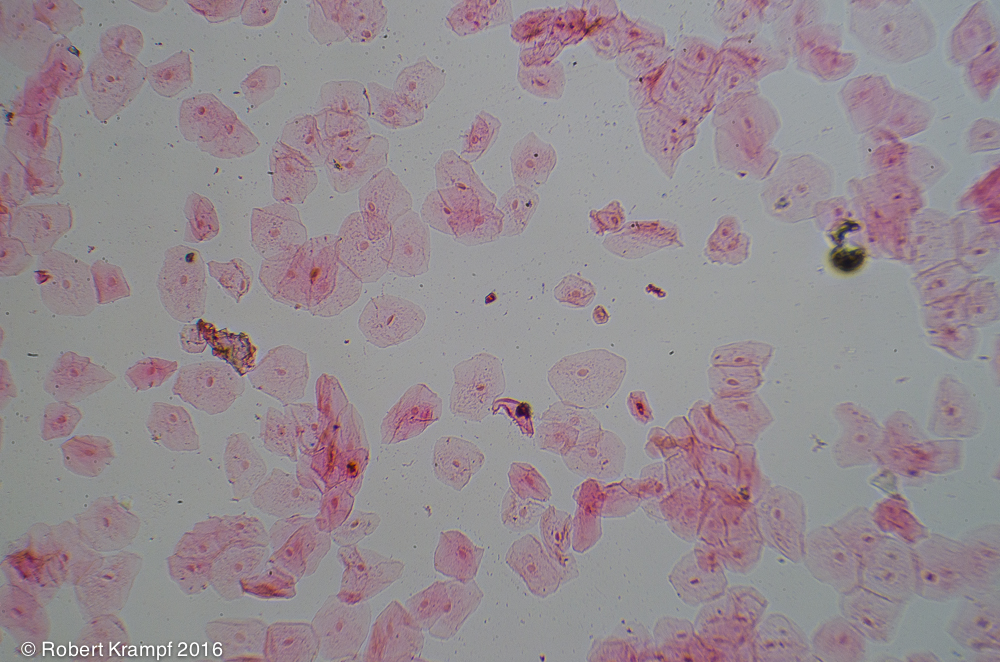
The dark spot in each of these cells contains genetic material called DNA. This part of the cell is called the:
-
Vacuole
No. A vacuole is used for storing water or nutrients, not DNA. -
Nucleus
Yes! The nucleus of the cell contains DNA. -
Chloroplast
No. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which is used in photosynthesis. -
Ribosome
No. Ribosomes are parts of the cell that assemble proteins.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.6.L.14.4 Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles.
| Osmosis | video, checked |
| Review Cells-4 | practice |
| Review Cells-1 | practice |
| Review Cells-2 | practice |
| Review Cells-3 | practice |
Utah
UT.7.III.1.c Differentiate between plant and animal cells based on cell wall and cell membrane.
| Review Cells-1 | practice |
| Review Cells-2 | practice |
NGSS
MS-LS1-2 Develop and use a model to describe the function of a cell as a whole and ways parts of cells contribute to the function.
| Osmosis | video, checked |
| Review Cells-4 | practice |
| Review Cells-1 | practice |
| Review Cells-2 | practice |
| Review Cells-3 | practice |
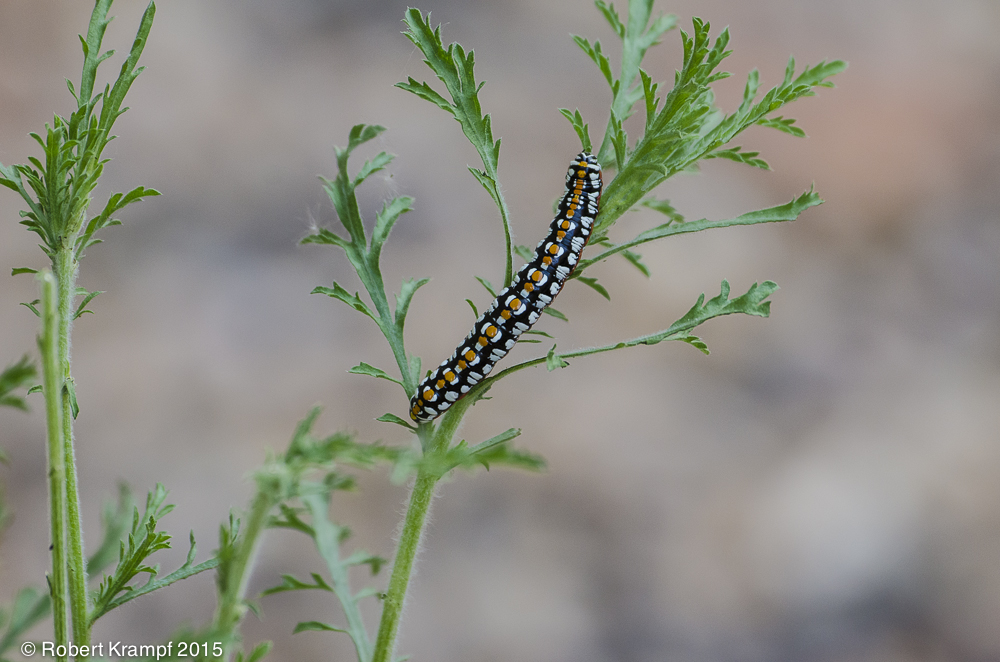

I found this caterpillar in my garden. Based on its bright colors, I decided not to pick it up. Why would it be so brightly colored?
-
To help it hide in flowers.
No. Its pattern of colors would not blend in with a flower. -
To warn away predators.
Yes! Many brightly colored animals are toxic or dangerous. They use their bright colors to warn potential predators that they taste bad, sting, or have some other characteristic that a predator would want to avoid.This is the caterpillar of a Hooded Owlet Moth. They eat the wild asters in our area, which gives them a very bitter taste that birds don't like.
-
To attract a mate.
No. Caterpillars do not mate. They must go through metamorphosis into a butterfly or moth before they can mate. -
To help it find food.
No. Most caterpillars eat plants, and bright colors would not help with that..
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.L.17.1 Compare and contrast adaptations displayed by animals and plants that enable them to survive in different environments such as life cycles variations, animal behaviors and physical characteristics.
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Review Plants-1 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-2 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
Utah
UT.6.V.1.b Compare characteristics common in observed organisms (e.g., color, movement, appendages, shape) and infer their function (e.g., green color found in organisms that are producers, appendages help movement).
| Onion Crystals | video |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
NGSS
3-LS4-2 Use evidence to construct an explanation for how the variations in characteristics among individuals of the same species may provide advantages in surviving, finding mates, and reproducing.
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Who Evolved on First? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-1 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
MS-LS1-4 Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful reproduction of animals and plants respectively.
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| How Does a Butterfly Fly? | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
