Here are some science questions from the Sixth, Seventh, and Eighth Grade Standards to help you test your knowledge of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time you reload the page.
* Click here to see only the most recently added questions.
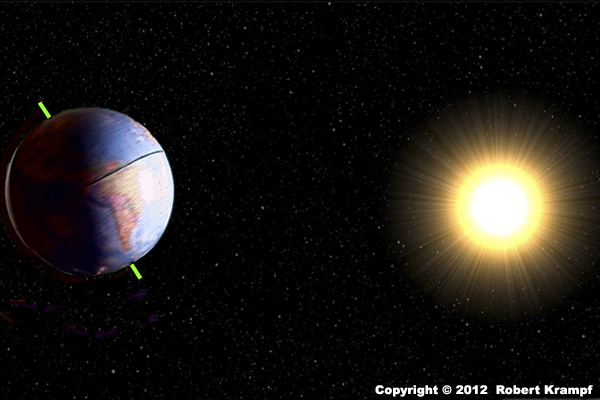
What season is Australia having in this graphic?
-
Spring
No. In the spring, the Earth's axis would not be tilted towards or away from the Sun. -
Summer
Yes! Australia is in the southern hemisphere, which is tilted towards the Sun. That tells us that it is summer there. -
Autumn
No. In the autumn, the Earth's axis would not be tilted towards or away from the Sun. -
Winter
No. Australia is in the southern hemisphere. If it was having winter, then the southern hemisphere would be tilted away from the Sun.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.5.1 Observe that the patterns of stars in the sky stay the same although they appear to shift across the sky nightly, and different stars can be seen in different seasons.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Space-5 | practice |
| Review Space-8 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
SC.8.E.5.9 Explain the impact of objects in space on each other including: 1. the Sun on the Earth including seasons and gravitational attraction 2. the Moon on the Earth, including phases, tides, and eclipses, and the relative position of each body.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
Utah
UT.6.II.2.e Use a model to explain why the seasons are reversed in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Space-5 | practice |
| Review Space-8 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
NGSS
5-ESS1-2 Represent data in graphical displays to reveal patterns of daily changes in length and direction of shadows, day and night, and the seasonal appearance of some stars in the night sky.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Finding Your Way | video, checked |
| Review Space-5 | practice |
| Review Space-8 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
MS-ESS1-1 Develop and use a model of the Earth-sun-moon system to describe the cyclic patterns of lunar phases, eclipses of the sun and moon, and seasons.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |

Which part of the food web do these termites belong to?
-
Producer.
No. A producer captures energy from sunlight, and stores it as food. To do that, the organism needs to contain chlorophyll. -
Primary Consumer.
No. Primary consumers eat producers. Termites do not eat live plants. -
Secondary Consumer
No. Secondary consumers eat other consumers. This butterfly does not eat animals. -
Decomposer
Yes! Termites are one of the few animals that can digest the cellulose from dead wood, thanks to special bacteria that live inside them. That makes termites very important as decomposers, but it also means that they can be a problem when we build things from wood.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
SC.7.L.17.1 Explain and illustrate the roles of and relationships among producers, consumers, and decomposers in the process of energy transfer in a food web.
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
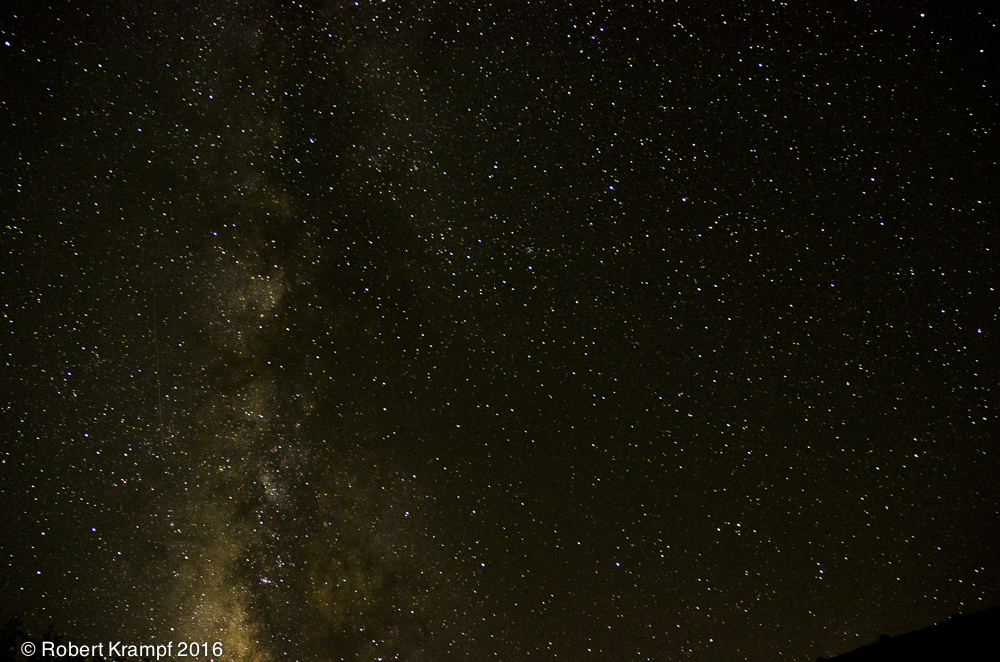

The light area on the left side of this photo is the Milky Way. What is the Milky Way?
-
A constellation.
No. The Milky Way contains many more stars than a constellation. -
A solar system.
No. A solar system only has one star, not a huge number of stars. -
A galaxy.
Yes! Our solar system is part of the Milky Way galaxy. When we lived in the city, the lights made it difficult to see the Milky Way. Now that we live far from city lights, it is amazingly easy to see. -
A universe.
No. The Milky Way is only a small part of the entire universe.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.E.5.1 Recognize that a galaxy consists of gas, dust, and many stars, including any objects orbiting the stars. Identify our home galaxy as the Milky Way.
| Review Space-2 | practice |
| Review Space-1 | practice |
| Review Space-10 | practice |
SC.8.E.5.3 Distinguish the hierarchical relationships between planets and other astronomical bodies relative to solar system, galaxy, and universe, including distance, size, and composition.
| Making a Scale Model of the Solar System | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| How Far is That Planet? | text page |
| Review Space-3 | practice |
| Review Space-2 | practice |
| Review Space-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.6.IV.1.c Compare the size of the Solar System to the size of the Milky Way galaxy.
| Review Space-2 | practice |
| Review Space-10 | practice |
NGSS
MS-ESS1-2 Develop and use a model to describe the role of gravity in the motions within galaxies and the solar system.
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
| Review Space-10 | practice |

I wanted to test a new fertilizer, to find the best concentration for my garden. I divided my garden into four sections and put a different amount of fertilizer in each section.
My test results showed that using 10 grams of fertilizer per gallon made the plants grow faster and bigger. To follow proper scientific guidelines, what should I do next?
-
Apply 10 grams of fertilizer per gallon to all the plants in my garden.
No. While that might make my garden grow well, it would not provide more evidence that this was the best mixture of fertilizer -
Do the same experiment over again.
Yes! Repetition is an important part of the scientific process. If my hypothesis is correct, I should get the same results every time I repeat the experiment. -
Do the same experiment, but use a different fertilizer.
No. Using a different fertilizer would be testing a different variable. I wanted to find the best concentration of the original fertilizer, so testing a different fertilizer would not help with that. -
Publish my results, so that other scientists could replicate my experiment.
No. Replication is an important step, but I should repeat my experiment several times to be sure that I get consistent results before I ask other scientists to try replicating it.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.2.N.1.4 Explain how particular scientific investigations should yield similar conclusions when repeated.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
SC.5.N.1.3: Recognize and explain the need for repeated experimental trials.
>>> Teacher Page: Nature of Science and Dissolving
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
SC.8.N.1.2 Design and conduct a study using repeated trials and replication.
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
3-5-ETS1-3 Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
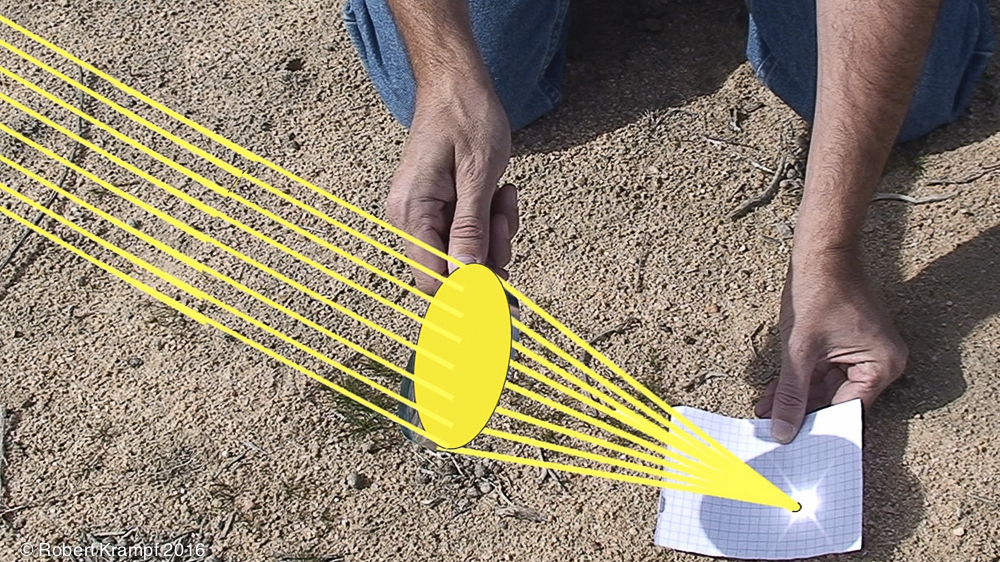
The yellow lines show how light is bent as it passes through a magnifying glass. This is an example of:
-
Absorption
No. The glass is clear, telling us that very little of the light is being absorbed. Absorption does not bend the light. -
Diffusion
No. Diffusion is the scattering of light as it is reflected in many different directions. Diffusion would make the rays of light go in many different directions. -
Refraction
Yes! Refraction bends light as it moves from one substance to another. As the light passes through the curved lens of the magnifying glass its path is changed, bending the rays towards the focal point. -
Reflection
No. While some light is reflected from the glass, it is not responsible for the bending of the light.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.3.P.10.3 Demonstrate that light travels in a straight line until it strikes an object or travels from one medium to another.
| Why Wet Things Turn Dark | video, checked |
| Growing Crystals Under the Microscope | video, free, learnalong, checked |
| Changing the Speed of Light | video |
| Why is Foam White? | video, checked |
| Microscopes: Growing Crystals | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Birefringence | video, free, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Polarized Light | video, free, Updated |
| Mirage | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Pinhole Eyeglasses | video, checked |
| A Long Lens | text page |
| Review Light-1 | practice |
| Review Light-2 | practice |
| Review Light-3 | practice |
| Review Light-4 | practice |
| Review Light-5 | practice |
SC.3.P.10.4 Demonstrate that light can be reflected, refracted, and absorbed.
| Looking for Rainbows | video |
| Why Wet Things Turn Dark | video, checked |
| Growing Crystals Under the Microscope | video, free, learnalong, checked |
| Changing the Speed of Light | video |
| Why is Foam White? | video, checked |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| Microscopes: Growing Crystals | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Birefringence | video, free, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Polarized Light | video, free, Updated |
| Mirage | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Pinhole Eyeglasses | video, checked |
| A Long Lens | text page |
| Sunlight, Energy, and Crayons | text page, free |
| Review Light-1 | practice |
| Review Light-2 | practice |
| Review Light-3 | practice |
| Review Light-4 | practice |
| Review Light-5 | practice |
SC.7.P.10.2 Observe and explain that light can be reflected, refracted, and/or absorbed.
| Pinhole Eyeglasses | video, checked |
| Why Wet Things Turn Dark | video, checked |
| Growing Crystals Under the Microscope | video, free, learnalong, checked |
| Finding Fat in Foods | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Changing the Speed of Light | video |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| Why is Foam White? | video, checked |
| Microscopes: Growing Crystals | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Birefringence | video, free, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Polarized Light | video, free, Updated |
| Mirage | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| A Long Lens | text page |
| Sunlight, Energy, and Crayons | text page, free |
| Review Light-1 | practice |
| Review Light-2 | practice |
| Review Light-3 | practice |
| Review Light-4 | practice |
| Review Light-5 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.IV.1.b Compare the transfer of energy (i.e., sound, light, earthquake waves, heat) through various mediums.
| Microwave Chocolate | video, checked |
| Spoon Bells | video, checked |
| The Singing Glass | video, checked |
| Why Wet Things Turn Dark | video, checked |
| The Science of Pizza | video, checked |
| Heating a Balloon | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Changing the Speed of Light | video |
| Doppler Effect | video, checked |
| Solar Power | video, checked |
| Sunglass Science: Birefringence | video, free, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Polarized Light | video, free, Updated |
| Noisy String | video, checked |
| Mirage | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| About Microwaves | video, checked |
| Comparing How Sound Moves Through Liquids and Gases | text page |
| Review Light-1 | practice |
| Review Light-2 | practice |
| Review Light-4 | practice |
| Review Light-5 | practice |
NGSS
1-PS4-3 Plan and conduct an investigation to determine the effect of placing objects made with different materials in the path of a beam of light.
| Pinhole Eyeglasses | video, checked |
| Why Wet Things Turn Dark | video, checked |
| Growing Crystals Under the Microscope | video, free, learnalong, checked |
| Sunprints | video |
| Changing the Speed of Light | video |
| Why is Foam White? | video, checked |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| Microscopes: Growing Crystals | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Birefringence | video, free, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Polarized Light | video, free, Updated |
| Mirage | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| A Color You Can't See | video, free, checked |
| A Long Lens | text page |
| Review Light-1 | practice |
| Review Light-2 | practice |
| Review Light-3 | practice |
| Review Light-4 | practice |
| Review Light-5 | practice |
MS-PS4-2 Develop and use a model to describe that waves are reflected, absorbed, or transmitted through various materials.
| Microwave Chocolate | video, checked |
| Why Wet Things Turn Dark | video, checked |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| Sunprints | video |
| Finding Fat in Foods | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Changing the Speed of Light | video |
| Why is Foam White? | video, checked |
| Sunglass Science: Birefringence | video, free, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Polarized Light | video, free, Updated |
| Mirage | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| About Microwaves | video, checked |
| A Long Lens | text page |
| Sunlight, Energy, and Crayons | text page, free |
| Review Light-1 | practice |
| Review Light-2 | practice |
| Review Light-4 | practice |
| Review Light-5 | practice |
