Here are some science questions to help you test your general science knowledge. They will also show you which of the Florida, Utah, and NGSS science standards each question is testing.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
Get 5 more random questions.
Would you rather see the most recently added questions?
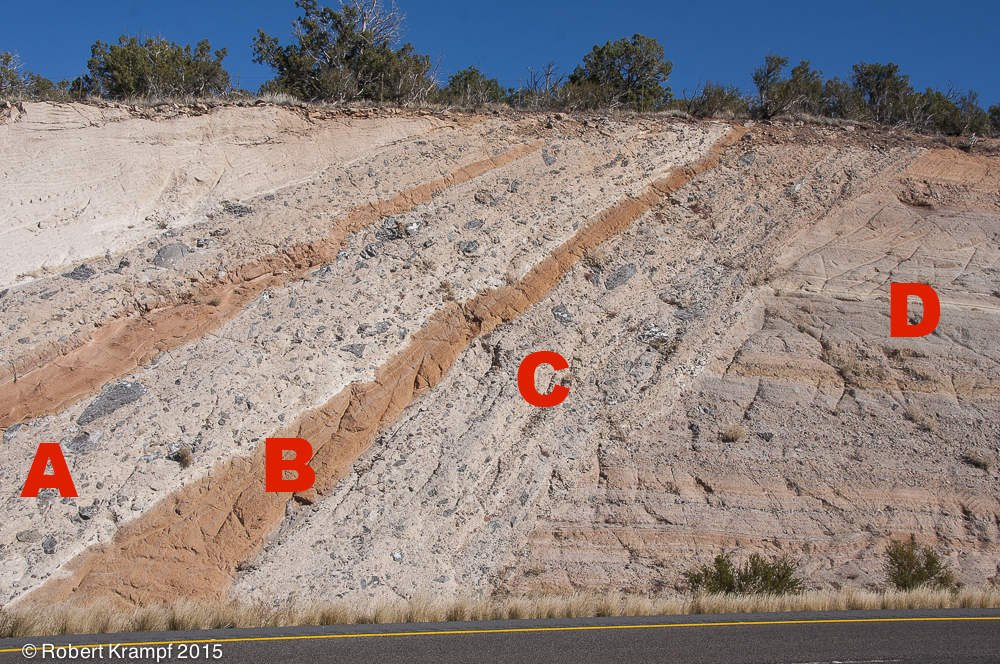

None of these layers have been turned upside down. Based on the Law of Superposition, which layer is the oldest?
-
A
No. Layer A is on top of layer B, so it is younger than layer B. That means that it is not the oldest. -
B
No. If you look at layer B, it is on top of layer C, which means that it is younger than layer C. B is not the oldest. -
C
No. Look closely at the top part of layer C. The top part of layer C is on top of part of layer D. That tells us that layer C is younger than layer D. -
D
Yes! This one is a bit tricky, because of the way the rocks were formed. Layer D formed first, as a flat, horizontal layer. Erosion weathered the left part of D away, forming a sloping hillside. Image the photo with layers A, B, and C erased, and it looks like a sloping hillside.Next, a nearby volcano erupted, spewing out lots of volcanic ash. The ash covered the hillside, forming layer C.
Next, lava from the volcano flowed down over the ash, forming layer B.
Later, the volcano erupted again, depositing another layer of volcanic ash to form layer A. After that, layer A was covered by another layer of lava, and then another layer of volcanic ash.
So A is the youngest, followed by B, then C, and D is the oldest.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.7.E.6.3 Identify current methods for measuring the age of Earth and its parts, including the law of superposition and radioactive dating.
| Imagining Geologic Time | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| Reading the Rocks | text page |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.III.3.c Explain why some sedimentary rock layers may not always appear with youngest rock on top and older rocks below (i.e., folding, faulting).
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
NGSS
4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns in rock formations and fossils in rock layers to support an explanation for changes in a landscape over time.
| Paleo Cookies | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Reading the Rocks: The Present is the Key to the Past | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
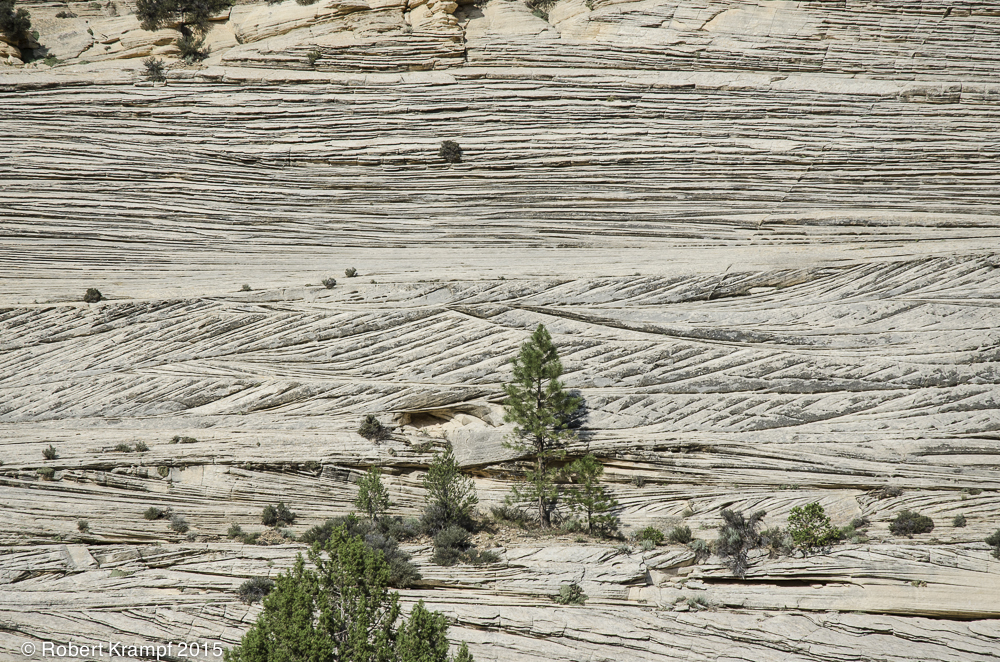

This is the Navajo Sandstone, a huge layer of rock that forms the cliff in our back yard. The strange patterns in the sandstone tell us that at the time they were formed, this area was a desert, and the sand formed sand dunes. What kind of rock is sandstone?
-
Igneous
No. Igneous rocks are formed from molten lava or magma, not from sand. -
Sedimentary
Yes! Sedimentary rocks are made up of bits of other rocks that have been deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity. This sand was deposited by the wind, making this a sedimentary rock. -
Metamorphic
No. Metamorphic rocks have been changed by heat and/or pressure. If this sandstone was exposed to tremendous heat and pressure, it could change into a metamorphic rock called quartzite. -
Sandstone is not a rock.
No. Sandstone is a naturally occurring solid that forms large layers in the Earth. It is a rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.d Classify common rocks found in Utah as sedimentary (i.e., sandstone, conglomerate, shale), igneous (i.e., basalt, granite, obsidian, pumice) and metamorphic (i.e., marble, gneiss, schist).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
UT.8.III.1.c Categorize rock samples as sedimentary, metamorphic, or igneous.
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
NGSS
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
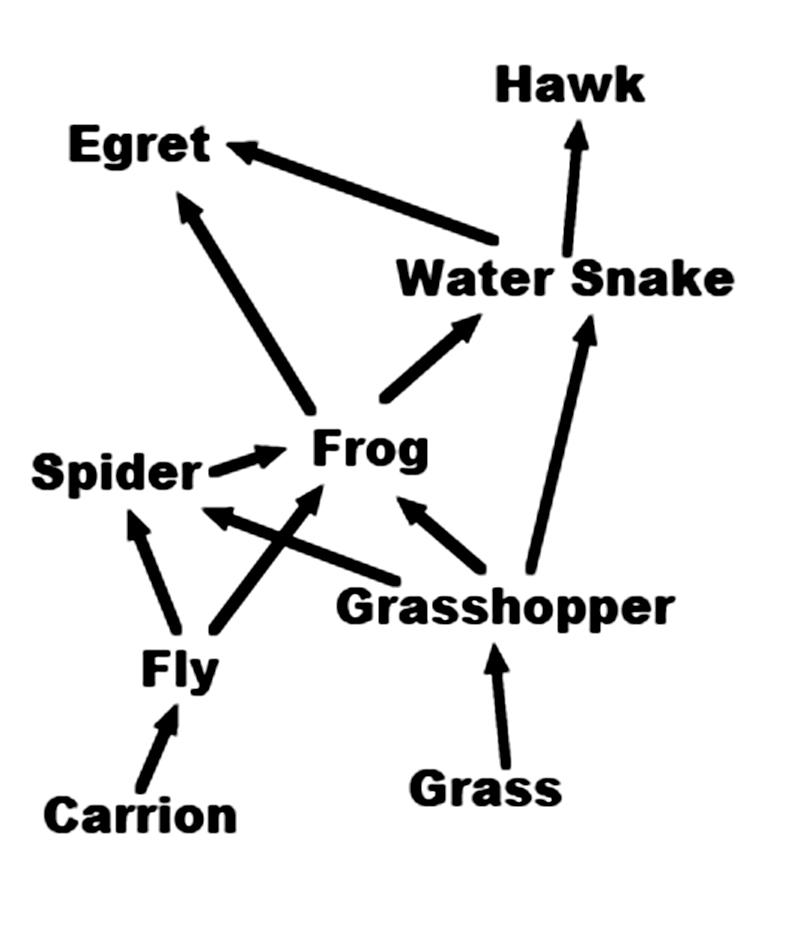
This is a simple chart showing how energy flows through some of the parts of a food web. For example, the arrow from the grass to the grasshopper shows that the grasshopper gets it energy by eating the grass.
The hawk gets its energy by eating the water snake, but there is no arrow leading from the hawk. What should the arrow from the hawk point to>
-
Egret
No. The egret does not eat hawks. -
Carrion
Yes! Carrion is dead animals. When the hawk eventually dies, flies will get their energy by eating the dead body. You could also draw arrows from all of the other animals to carrion. -
The Sun
No. The Sun is not on the chart, and The Sun does not get its energy from the hawk. -
There should not be an arrow leading from the hawk.
No. Energy cannot be destroyed. It always goes back into the system.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
SC.8.L.18.4 Cite evidence that living systems follow the Laws of Conservation of Mass and Energy.
| Thoughts on Trees | text page |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
Which of the following is a vertebrate?
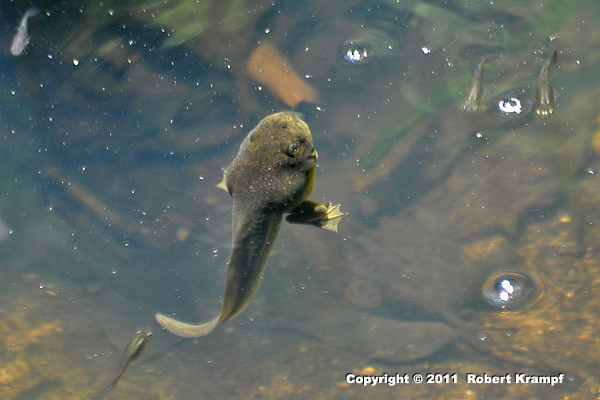




-
A: crab
No. Crabs have an exoskeleton. They are arthropods, which are invertebrates. -
B: starfish
No. Starfish do not have a vertebral column or a notochord. They are echinoderms, which are invertebrates. -
C: fly
No. Flies have an exoskeleton. They are insects, which are invertebrates. -
D: tadpole
Yes! Tadpoles are amphibians. They have an internal skeleton, which includes a vertebral column. They are vertebrates.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.3.L.15.1 Classify animals into major groups (mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, arthropods, vertebrates and invertebrates, those having live births and those which lay eggs) according to their physical characteristics and behaviors.
| Feathers | video, checked |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Scientific Names | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Classify-2 | practice |
| Review Classify-1 | practice |
| Review Classify-3 | practice |
SC.6.L.15.1 Analyze and describe how and why organisms are classified according to shared characteristics with emphasis on the Linnaean system combined with the concept of Domains.
| Scientific Names | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Classify-2 | practice |
| Review Classify-1 | practice |
| Review Classify-3 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.V.3.b Use a simple classification system to classify unfamiliar Utah plants or animals (e.g., fish/amphibians/reptile/bird/mammal, invertebrate/vertebrate, tree/shrub/grass, deciduous/conifers).
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Scientific Names | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Classify-2 | practice |
| Review Classify-1 | practice |
| Review Classify-3 | practice |
UT.7.V.2.c Generalize rules for classification.
| Scientific Names | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Classify-2 | practice |
| Review Classify-1 | practice |
| Review Classify-3 | practice |
NGSS

When you break the mineral calcite, it breaks into shapes with flat, smooth sides. This is an example of:
-
Cleavage
Yes! A mineral has cleavage when it breaks to form flat, smooth surfaces. -
Fracture
No. There are different kinds of fractures, but none of them form flat, smooth surfaces. -
Conchoidal
No. A conchoidal fracture is the shell-shaped break that is commonly seen when glass breaks. A conchoidal fracture is not flat.

-
Hardness
No. Hardness tells us how easily a mineral can be scratched, not how it breaks.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.2 Identify the physical properties of common earth-forming minerals, including hardness, color, luster, cleavage, and streak color, and recognize the role of minerals in the formation of rocks.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Minerals Around You | text page, learnalong, checked |
| Review Minerals-1 | practice |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.b Observe rocks using a magnifying glass and draw shapes and colors of the minerals.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
UT.8.III.1.b Observe and describe the minerals found in rocks (e.g., shape, color, luster, texture, hardness).
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Review Minerals-1 | practice |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties.
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| Making Turmeric Paper | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Floating Bubbles | video, checked |
| Finding Fat in Foods | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Fireworks Colors | video |
| Iron Cereal | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Density: Ice, Oil, and Water | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 1 | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 2 | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| A Cool Change | text page |
| Acid Hunt | text page |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
