Here are some science questions to help you test your general science knowledge. They will also show you which of the Florida, Utah, and NGSS science standards each question is testing.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
Get 5 more random questions.
Would you rather see the most recently added questions?

This is Halite, also known as table salt. It was formed when ancient seas dried up, leaving layers of salt behind. What kind of rock is it?.
-
Igneous
No. Igneous rocks formed from magma or lava. The Halite was not melted, and is not an igneous rock. -
Sedimentary
Yes! Sedimentary rocks are deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity, and they often contain fossils. Halite was deposited in large layers by water, which means that it is a sedimentary rock. Halite is also a mineral, and is one of the few rocks/minerals that we eat. -
Metamorphic
No. Metamorphic rocks have been changed by heat and pressure from a different kind of rock. It is not metamorphic. -
Halite is not a rock.
No. Halite is a naturally occurring solid that forms large layers in the Earth. Halite is a rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
SC.7.E.6.2 Identify the patterns within the rock cycle and relate them to surface events (weathering and erosion) and sub-surface events (plate tectonics and mountain building).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.a Describe the differences between minerals and rocks.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
NGSS
4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns in rock formations and fossils in rock layers to support an explanation for changes in a landscape over time.
| Paleo Cookies | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Reading the Rocks: The Present is the Key to the Past | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
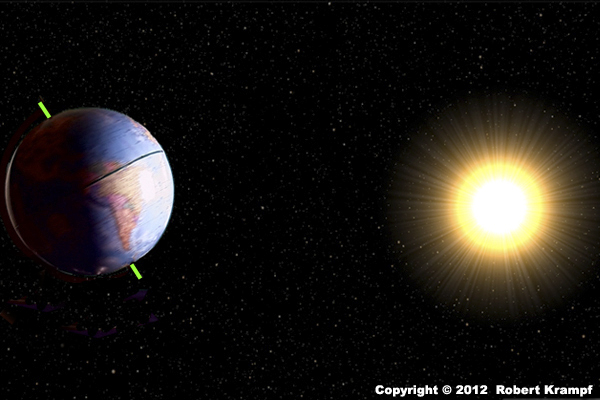
The Earth stays in orbit around the Sun because:
-
The Sun's gravity pulls on the Earth
This is only part of the answer. -
The Earth's gravity pulls on the Sun
This is only part of the answer. -
The gravity of the Sun and the Earth pull on each other
Yes! The gravitational attraction between the Earth and the Sun is a result of both the Sun pulling on the Earth and the Earth pulling on the Sun. -
Gravity does not keep the Earth in its orbit.
No. Without the pull of gravity, the Earth would continue moving in a straight path instead of curving around the Sun.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.P.13.1 Identify familiar forces that cause objects to move, such as pushes or pulls, including gravity acting on falling objects.
| The Slow Race | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Magic Coin | video |
| Making a Compass | video, checked |
| Torque | video |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
SC.8.E.5.9 Explain the impact of objects in space on each other including: 1. the Sun on the Earth including seasons and gravitational attraction 2. the Moon on the Earth, including phases, tides, and eclipses, and the relative position of each body.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
SC.6.P.13.2 Explore the Law of Gravity by recognizing that every object exerts gravitational force on every other object and that the force depends on how much mass the objects have and how far apart they are.
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Force, Pressure, and Shoes | video, checked |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
Utah
UT.3.IV.2.c Pose questions about gravity and forces.
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Force, Pressure, and Shoes | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Energy-8 | quest |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
UT.6.III.3.a Describe the forces holding Earth in orbit around the sun, and the moon in orbit around Earth.
| Review Space-13 | quest |
NGSS
MS-ESS1-2 Develop and use a model to describe the role of gravity in the motions within galaxies and the solar system.
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
| Review Space-10 | practice |
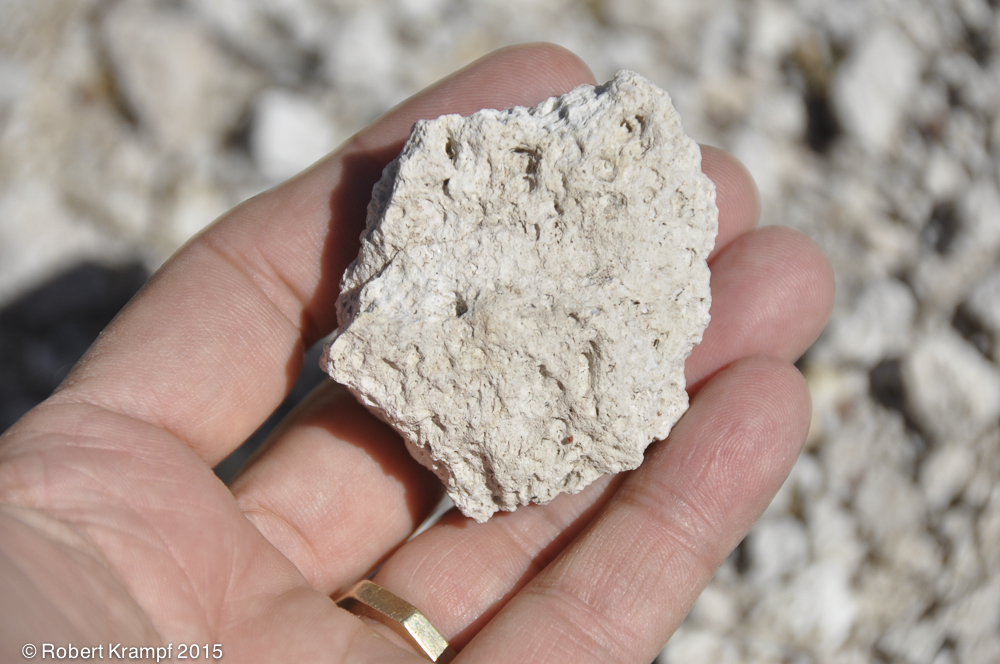

This is called Pumice. It is formed when magma reaches the surface, and reduced pressure lets gas bubbles escape. When it cools, it has so many trapped air bubbles that it will actually float in water. What kind of rock is it?.
-
Igneous
Yes! Igneous rocks formed from magma or lava. This is an igneous rock. -
Sedimentary
No. Sedimentary rocks are deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity, and they often contain fossils. This is not a sedimentary rock. -
Metamorphic
No. Metamorphic rocks have been changed by heat and pressure from a different kind of rock. Instead of being changed, this got hot enough to completely melt, so it is not metamorphic. -
Pumice is not a rock.
No. Pumice is a naturally occurring solid that forms large layers in the Earth. Pumice is a rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
SC.7.E.6.2 Identify the patterns within the rock cycle and relate them to surface events (weathering and erosion) and sub-surface events (plate tectonics and mountain building).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.a Describe the differences between minerals and rocks.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
NGSS
4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns in rock formations and fossils in rock layers to support an explanation for changes in a landscape over time.
| Paleo Cookies | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Reading the Rocks: The Present is the Key to the Past | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |

When Nancy and I moved from Florida to our new home in Utah, we found that many of the flowers we grew in Florida would not grow well here. Why?
-
The soil is different.
This is part of the answer. The soil here is mostly sand, and is very alkaline. The soil in Florida had much more organic matter and was more acidic. Plants that need rich soil do not grow well here. -
The climate is different.
This is part of the answer. The climate in Utah is very different from Florida. The winters are MUCH colder (down to -20°F) and the summers are MUCH hotter (up to 125°F). The climate here is also much drier. When we lived in Jacksonville, FL, we got about 52 inches of rainfall each year. Here in Utah, we only get about 14 inches of rainfall each year. Some of the plants from Florida can grow here, but the ones that cannot stand the cold, heat, and dry conditions do not. -
The animals are different.
This is part of the answer. The wildlife here is much different from the animals in Florida. There are insects here that eat plants that were not bothered by Florida insects. There are rock squirrels, western pocket gophers, jack rabbits, mule deer, and many other animals here that love to eat many kinds of flowers. Plants that do not have a bitter taste, spines, or other ways to discourage animals do not do well here. -
All of the above.
Yes! All of the answers are correct. When you take an organism from one environment and put it into another, you may see different results. If the organism is not adapted for the new environment, it may die or not grow well. If it is very well adapted to the new environment, it may take over, crowding out some of the native organisms.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.L.17.1 Compare and contrast adaptations displayed by animals and plants that enable them to survive in different environments such as life cycles variations, animal behaviors and physical characteristics.
| Onion Crystals | video |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Plants-1 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-2 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
SC.5.L.15.1 Describe how, when the environment changes, differences between individuals allow some plants and animals to survive and reproduce while others die or move to new locations.
| Who Evolved on First? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Adaptation-1 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
SC.7.L.15.3 Explore the scientific theory of evolution by relating how the inability of a species to adapt within a changing environment may contribute to the extinction of that species.
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.V.2.b Cite examples of physical features that allow particular plants and animals to live in specific environments (e.g., duck has webbed feet, cactus has waxy coating).
| Hunting with an Umbrella | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| How Does a Butterfly Fly? | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
UT.5.V.2.c Describe how a particular physical attribute may provide an advantage for survival in one environment but not in another (e.g., heavy fur in arctic climates keep animals warm whereas in hot desert climates it would cause overheating; flippers on such animals as sea lions and seals provide excellent swimming structures in the water but become clumsy and awkward on land; cacti retain the right amount of water in arid regions but would develop root rot in a more temperate region; fish gills have the ability to absorb oxygen in water but not on land).
| Review Adaptation-1 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
UT.6.V.1.b Compare characteristics common in observed organisms (e.g., color, movement, appendages, shape) and infer their function (e.g., green color found in organisms that are producers, appendages help movement).
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
UT.7.IV.2.a Predict why certain traits (e.g., structure of teeth, body structure, coloration) are more likely to offer an advantage for survival of an organism.
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| Who Evolved on First? | text page, free, checked |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-1 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-2 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
NGSS
3-LS4-2 Use evidence to construct an explanation for how the variations in characteristics among individuals of the same species may provide advantages in surviving, finding mates, and reproducing.
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Who Evolved on First? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Adaptation-1 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
MS-LS1-4 Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful reproduction of animals and plants respectively.
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| How Does a Butterfly Fly? | text page, free |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
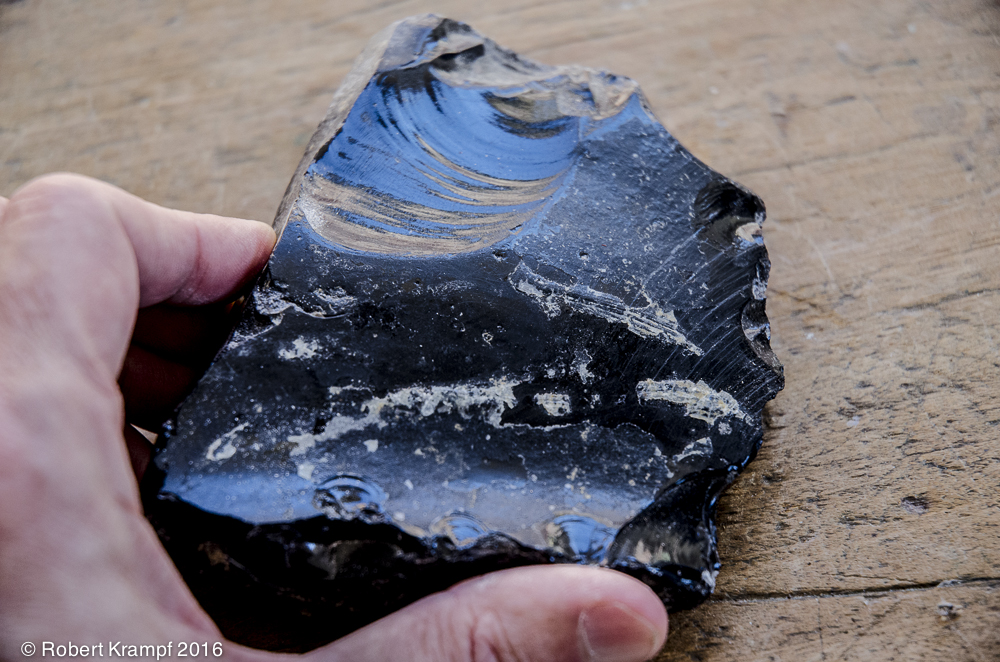

This is called Obsidian. It is formed from molten lava that cools so quickly that it forms a natural glass instead of crystals. What kind of rock is it?.
-
Igneous
Yes! Igneous rocks formed from magma or lava. This is an igneous rock. -
Sedimentary
No. Sedimentary rocks are deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity, and they often contain fossils. This is not a sedimentary rock. -
Metamorphic
No. Metamorphic rocks have been changed by heat and pressure from a different kind of rock. Instead of being changed, this got hot enough to completely melt, so it is not metamorphic. -
Obsidian is not a rock.
No. Obsidian is a naturally occurring solid that forms large layers in the Earth. Obsidian is a rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
SC.7.E.6.2 Identify the patterns within the rock cycle and relate them to surface events (weathering and erosion) and sub-surface events (plate tectonics and mountain building).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.a Describe the differences between minerals and rocks.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
NGSS
4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns in rock formations and fossils in rock layers to support an explanation for changes in a landscape over time.
| Paleo Cookies | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Reading the Rocks: The Present is the Key to the Past | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
