Here are the most recent questions from the Test Your Science Knowledge series.
If you would rather, you can get a random selection from all of the questions.

I wanted to test different amounts of fertilizer to see which was best for growing grass. I mixed water with different amounts of fertilizer, and then added sodium polyacrylate to change it into a gel. Then I sprinkled the grass seeds on top, and waited for them to grow.
I really need a control group for this experiment. What would I use for a control?
-
Water, fertilizer, and grass seed, without any sodium polyacrylate.
No. For the control, we want to skip the thing we are testing for. We are not testing changes caused by the amount of sodium polyacrylate. -
Water, sodium polyacrylate, and grass seed, without any fertilizer.
Yes! We are testing to see how different amounts of fertilizer change the growth of the grass. The amount of fertilizer is the variable we are testing, so the control group should not have any fertilizer. -
Water, sodium polyacrylate, and fertilizer, without any grass seed.
No. For the control, we want to skip the thing we are testing for. We are not testing changes caused by the amount of grass seed, and we know that no grass will grow if we do not have any seeds. -
Sodium polyacrylate, fertilizer, and grass seed, without any water.
No. For the control, we want to skip the thing we are testing for. We are not testing changes caused by the amount of water.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.1.4 Identify a control group and explain its importance in an experiment.
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.4 Identify test variables (independent variables) and outcome variables (dependent variables) in an experiment.
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
3-5-ETS1-3 Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
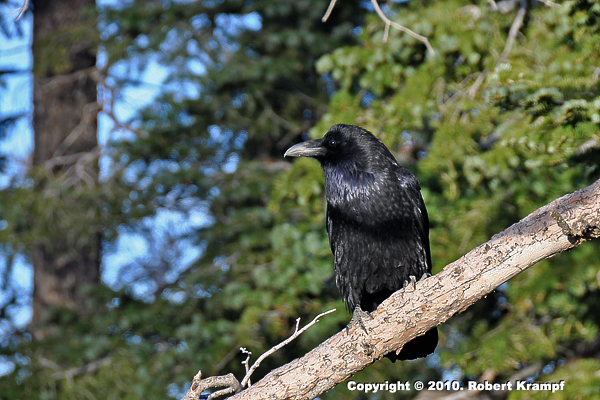

The Common Raven is often a scavenger, but its beak is not strong enough to tear through the thick hide of a winter-killed deer.
It will sit near the carcass and call loudly, attracting other ravens. As the mob gathers, they start making distress calls. That usually attracts a large predator, such as a wolf or coyote. They wait until the predator tears into the carcass.
At that point, 3 or 4 of them will start harassing the predator, keeping its attention, while the other ravens steal parts of the carcass. They then share what they get with the ravens that kept the predator busy.
This is an example of what kind of relationship?
-
mutualism
Yes! In mutualism, both organisms benefit. The ravens help the predator find the carcass, and the predator tears it open so that the ravens can eat some too. Both get a benefit from the relationship. -
commensalism
No. In commensalism, one organism benefits, and the other is not affected. In this case, the ravens and the predator both benefit. -
parasitism
No. For parasitism, one organism benefits, and the other is harmed. Neither the raven nor the predator is harmed by this relationship. -
predation
No. In predation, one organism eats another. Neither the raven nor the predator gets eaten in this relationship.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.7.L.17.2 Compare and contrast the relationships among organisms such as mutualism, predation, parasitism, competition, and commensalism.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
NGSS
MS-LS2-2 Construct an explanation that predicts patterns of interactions among organisms across multiple ecosystems.
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
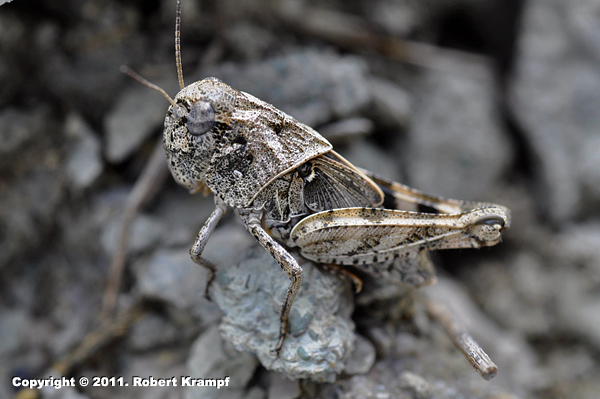
Why does this grasshopper have such small wings?
-
Because this species does not fly.
No. This species of grasshopper does fly. -
Because it has a mutation.
No. This is a normal grasshopper, not a mutant. -
Because it is a cricket, not a grasshopper.
No. This is a grasshopper. -
Because it is not an adult.
Yes! Grasshoppers have incomplete metamorphosis. The immature grasshoppers look similar to adults, but have some differences. The immature stages of the grasshopper has small wings, but the adult stage has large, functional wings.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.2.L.16.1 Observe and describe major stages in the life cycles of plants and animals, including beans and butterflies.
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-4 | practice |
SC.4.L.16.4 Compare and contrast the major stages in the life cycles of Florida plants and animals, such as those that undergo incomplete and complete metamorphosis, and flowering and nonflowering seedbearing
plants.
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Creating a Sprout Guide | text page, photography, free |
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-4 | practice |
Utah
UT.5.V.1.c Compare various examples of offspring that do not initially resemble the parent organism but mature to become similar to the parent organism (e.g., mealworms and darkling beetles, tadpoles and frogs, seedlings and vegetables, caterpillars and butterflies).
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-4 | practice |
NGSS
1-LS3-1 Make observations to construct an evidence-based account that young plants and animals are like, but not exactly like, their parents.
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
3-LS1-1 Develop models to describe that organisms have unique and diverse life cycles but all have in common birth, growth, reproduction, and death.
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
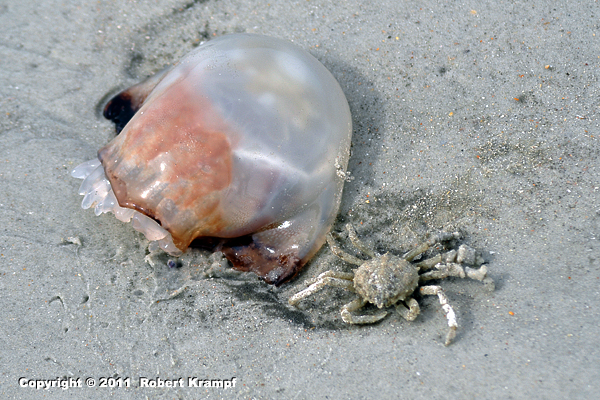

Cannonball Jelly fish are excellent swimmers, and Portly Spider Crabs often hitch a ride on them. What type of relationship is that?
-
mutualism
No. In mutualism, both organisms benefit. The jellyfish gets no benefit from the crab's hitchhiking. -
commensalism
Yes. In commensalism, one organism (the crab) benefits, and the other (jellyfish) is not affected. The crab gets free transportation, and the jellyfish is not helped or harmed. -
parasitism
No. For parasitism, one organism benefits, and the other is harmed. Neither the crab nor the jellyfish is harmed by this relationship. -
predation
No. In predation, one organism eats another. Neither the crab nor the jellyfish gets eaten in this relationship.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.7.L.17.2 Compare and contrast the relationships among organisms such as mutualism, predation, parasitism, competition, and commensalism.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
NGSS
MS-LS2-2 Construct an explanation that predicts patterns of interactions among organisms across multiple ecosystems.
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |

I used this piece of calcite to scratch this penny. Then I used the penny to scratch the piece of calcite. What does that tell us?
-
It tells us that I did the test wrong.
No. The test was done correctly. -
It tells us that they both have the same hardness.
Yes! You test the hardness of a mineral by testing to see what will scratch it. If two substances scratch each other, they have the same hardness. -
It tells us that calcite is not a mineral.
No. Scratching a specimen will not tell you if it is a mineral. -
It tells us that calcite has cleavage.
No. You do not test for cleavage by scratching a mineral.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.2 Identify the physical properties of common earth-forming minerals, including hardness, color, luster, cleavage, and streak color, and recognize the role of minerals in the formation of rocks.
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Minerals Around You | text page, learnalong, checked |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
| Review Minerals-1 | practice |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.b Observe rocks using a magnifying glass and draw shapes and colors of the minerals.
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
UT.8.III.1.b Observe and describe the minerals found in rocks (e.g., shape, color, luster, texture, hardness).
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
| Review Minerals-1 | practice |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties.
| Density: Ice, Oil, and Water | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 1 | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 2 | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| Making Turmeric Paper | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Floating Bubbles | video, checked |
| Finding Fat in Foods | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Fireworks Colors | video |
| Iron Cereal | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| A Cool Change | text page |
| Acid Hunt | text page |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
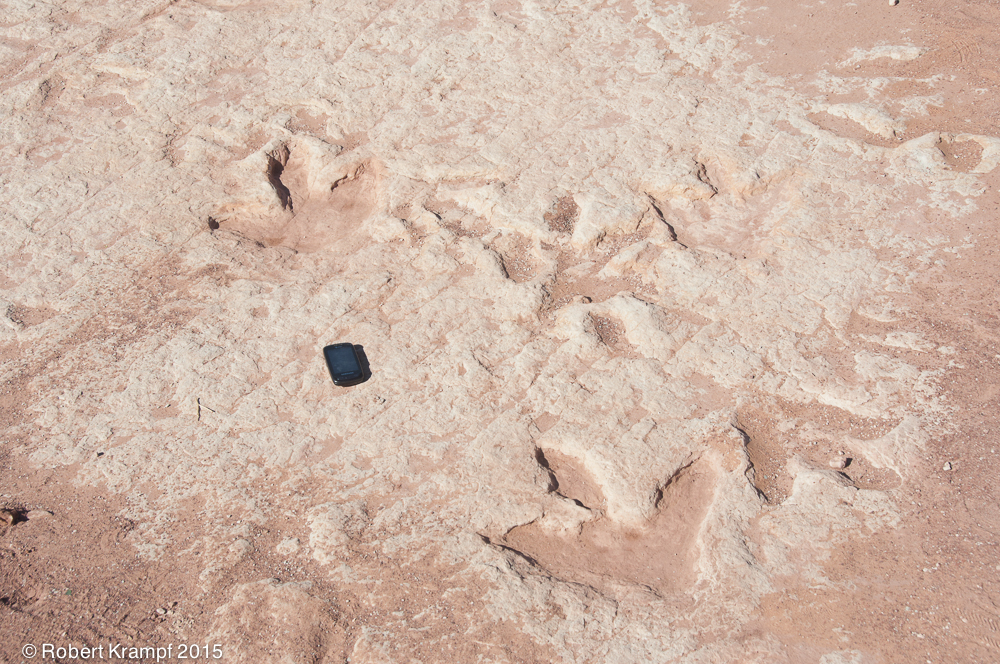

This layer of rock contains fossilized tracks from a dinosaur (Dilophosaurus). The black object is my cell phone for size reference. What kind of rock is it?
-
Igneous
No. Igneous rocks formed from magma or lava. An igneous rock would not have fossilized dinosaur tracks. -
Sedimentary
Yes! Sedimentary rocks are deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity, and they often contain fossils. The presence of fossils is one of the indications that a rock is probably sedimentary. -
Metamorphic
No. Metamorphic rocks have been changed by heat and pressure from a different kind of rock. The metamorphic process would have destroyed the tracks. -
It is not rock.
No. These dinosaur tracks are in rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.d Classify common rocks found in Utah as sedimentary (i.e., sandstone, conglomerate, shale), igneous (i.e., basalt, granite, obsidian, pumice) and metamorphic (i.e., marble, gneiss, schist).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
UT.8.III.1.c Categorize rock samples as sedimentary, metamorphic, or igneous.
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
NGSS
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
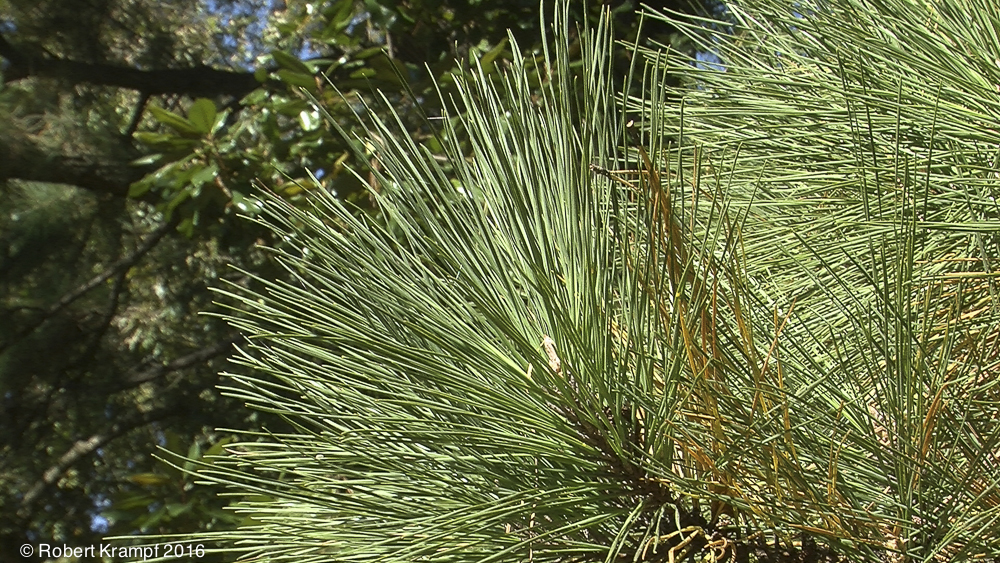

Pine trees do not have flowers. What structure do they have that servers the same purpose?
-
Needles
No. Pine needles are a kind of leaf. They are not used for reproduction. -
Cones
Yes! Pine cones produce pollen and seeds, just as flowers do in flowering plants. -
Fruit
No. Fruit are used for dispersing seeds, not for pollination. -
Buds
No. Pine tree buds produce needles. They are not involved in reproduction.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.3.L.15.2 Classify flowering and nonflowering plants into major groups such as those that produce seeds, or those like ferns and mosses that produce spores, according to their physical characteristics.
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
SC.3.L.14.1 Describe structures in plants and their roles in food production, support, water and nutrient transport, and reproduction.
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Heartless Plants | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Smell the Flowers | text page |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
SC.4.L.16.1 Identify processes of sexual reproduction in flowering plants, including pollination, fertilization (seed production), seed dispersal, and germination.
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
4-LS1-1 Construct an argument that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction.
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Bird Bones | video, free |
| Feathers | video, checked |
| Heartless Plants | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Eye Shine | text page |
| How Does a Butterfly Fly? | text page, free |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-1 | practice |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
MS-LS1-4 Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful reproduction of animals and plants respectively.
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| How Does a Butterfly Fly? | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
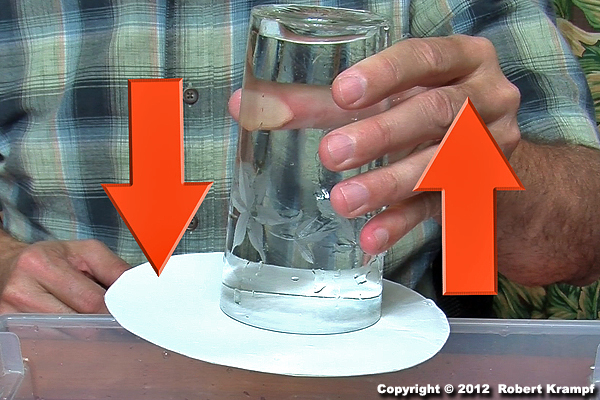

I put a paper plate on top of a glass of water. I turned it over, and the water stayed in the glass.
The weight of the water is pushing down on the paper plate, but the plate stays in the glass because the pull of gravity is being balanced by another force. What is that force?
-
Attraction
No. The slight attraction between the water and the glass is not enough to balance the pull of gravity. -
Air pressure
Yes! Because the plate is keeping outside air from entering the glass, outside air pressure is keeping the plate in place. As long as the outside air pressure is enough to balance the weight of the water and the plate, it will stay in place. If you made a small hole in the glass to let outside air get in, that would unbalance things, and the water would fall out. -
Surface tension
No. The water tension at the surface of the water would not balance the force of gravity. -
The weight of the paper card
No. Gravity is pulling down on the paper plate and the water. The weight of the paper does not help balance the force of gravity.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.2.P.13.3 Recognize that objects are pulled toward the ground unless something holds them up.
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |
SC.3.E.5.4 Explore the Law of Gravity by demonstrating that gravity is a force that can be overcome.
| Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Force, Pressure, and Shoes | video, checked |
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| More Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |
SC.5.P.13.4 Investigate and explain that when a force is applied to an object but it does not move, it is because another opposing force is being applied by something in the environment so that the forces are balanced.
| Newton's First Law of Motion | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 2 | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 1 | video, checked |
| Science Friction | video, checked |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| More Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Science of Balance | video, checked |
| The Old Tablecloth Trick | video |
| Force, Pressure, and Shoes | video, checked |
| Bernoulli Effect | video |
| Hanging a Hammer | video, checked |
| Torque | video |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Exploring Friction | text page |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |
SC.6.P.13.3 Investigate and describe that an unbalanced force acting on an object changes its speed, or direction of motion, or both.
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 2 | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 1 | video, checked |
| Science Friction | video, checked |
| More Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Bernoulli Effect | video |
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Torque | video |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |
Utah
UT.3.III.2.c Compare the relative effects of forces of different strengths on an object (e.g., strong wind affects an object differently than a breeze).
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 2 | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 1 | video, checked |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| The Old Tablecloth Trick | video |
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Newton's First Law of Motion | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |
UT.4.II.1.c Investigate evidence that air is a substance (e.g., takes up space, moves as wind, temperature can be measured).
| Nephoscope | video, checked |
| Air Space | video |
| Crushed Can | video, checked |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |
NGSS
3-PS2-1 Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence of the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces on the motion of an object.
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 2 | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 1 | video, checked |
| Science Friction | video, checked |
| More Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Force, Pressure, and Shoes | video, checked |
| Bernoulli Effect | video |
| The Slow Race | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Torque | video |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |
MS-PS2-2 Plan an investigation to provide evidence that the change in an object’s motion depends on the sum of the forces on the object and the mass of the object.
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Newton's First Law of Motion | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 2 | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 1 | video, checked |
| Science Friction | video, checked |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| More Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Science of Balance | video, checked |
| The Old Tablecloth Trick | video |
| Bernoulli Effect | video |
| Smoke Rings | video |
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| The Difference Between Weight and Mass | video, checked |
| Torque | video |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |
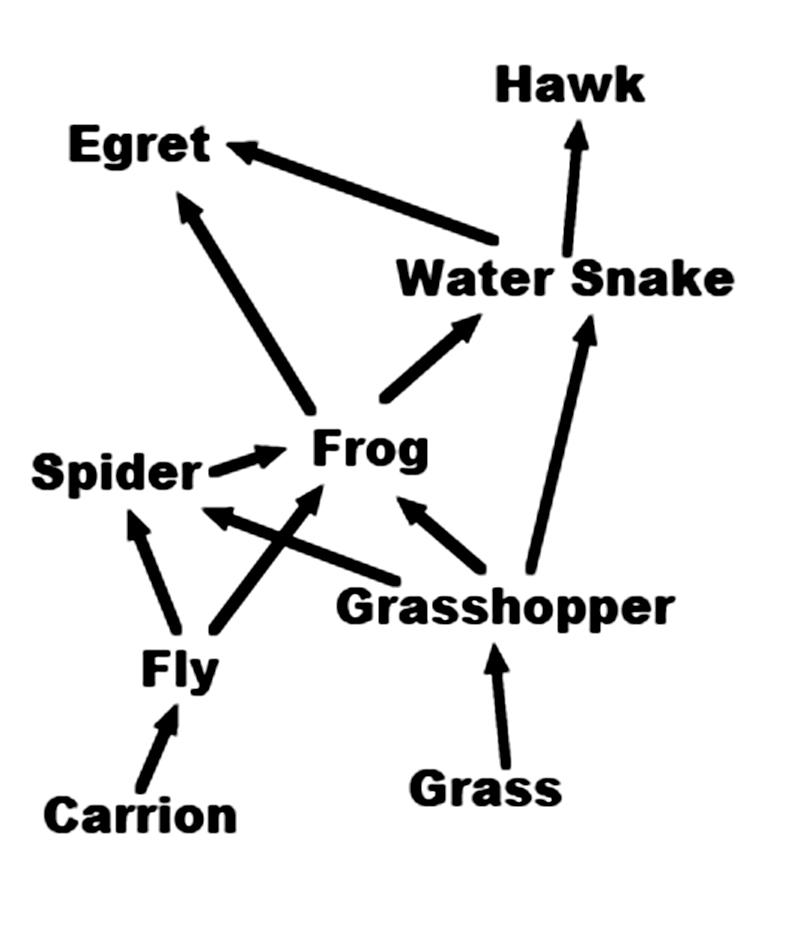
This is a simple chart showing how energy flows through some of the parts of a food web. For example, the arrow from the grass to the grasshopper shows that the grasshopper gets it energy by eating the grass.
The hawk gets its energy by eating the water snake, but there is no arrow leading from the hawk. What should the arrow from the hawk point to>
-
Egret
No. The egret does not eat hawks. -
Carrion
Yes! Carrion is dead animals. When the hawk eventually dies, flies will get their energy by eating the dead body. You could also draw arrows from all of the other animals to carrion. -
The Sun
No. The Sun is not on the chart, and The Sun does not get its energy from the hawk. -
There should not be an arrow leading from the hawk.
No. Energy cannot be destroyed. It always goes back into the system.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
SC.8.L.18.4 Cite evidence that living systems follow the Laws of Conservation of Mass and Energy.
| Thoughts on Trees | text page |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
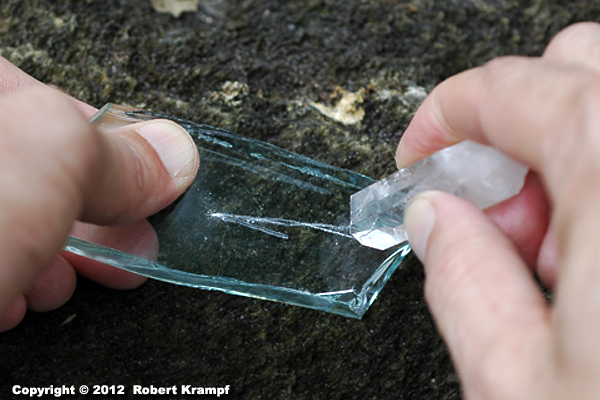

I used this piece of quartz to scratch a piece of glass. What was I testing?
-
Streak
No. To test streak, you rub the mineral on a white tile, to see its color when it is powdered. -
Fracture
No. Fracture is one way that minerals can break. I am not breaking the mineral. -
Hardness
Yes. Hardness is measured by scratching other substances, such as your fingernail, copper, and glass. This quartz scratches the glass, which tells us it has a hardness or 5.5 or more. Actually, the hardness of quartz is 7, quite a bit harder than glass. -
Cleavage
No. Cleavage is one of the ways that minerals can break. I am not breaking the mineral.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.2 Identify the physical properties of common earth-forming minerals, including hardness, color, luster, cleavage, and streak color, and recognize the role of minerals in the formation of rocks.
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Minerals Around You | text page, learnalong, checked |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
| Review Minerals-1 | practice |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.b Observe rocks using a magnifying glass and draw shapes and colors of the minerals.
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
UT.8.III.1.b Observe and describe the minerals found in rocks (e.g., shape, color, luster, texture, hardness).
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
| Review Minerals-1 | practice |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties.
| Density: Ice, Oil, and Water | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 1 | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 2 | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| Making Turmeric Paper | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Floating Bubbles | video, checked |
| Finding Fat in Foods | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Fireworks Colors | video |
| Iron Cereal | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| A Cool Change | text page |
| Acid Hunt | text page |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
