Here are some science questions from the Standards for Grades 2-5 to help you test your knowledge of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time you reload the page.
* Click here to see only the most recently added questions.

Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of ALL mammals?
-
All mammals have hair.
No. All mammals DO have hair. Even whales and dolphins have some hair on their skin. -
All mammals give birth to live young.
Yes! While most species of mammals give birth to live young, a few (platypus, echidna) lay eggs. -
All mammals have mammary glands.
No. All mammals DO have mammary glands. In females, these glands can produce milk to feed their young. -
All mammals have three bones in their inner ear.
No. All mammals DO have three bones in their inner ear. These bones are called the malleus, the incus, and the stapes. They transfer vibration from the ear drum to the inner ear.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.3.L.15.1 Classify animals into major groups (mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, arthropods, vertebrates and invertebrates, those having live births and those which lay eggs) according to their physical characteristics and behaviors.
| Feathers | video, checked |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Scientific Names | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Classify-2 | practice |
| Review Classify-1 | practice |
| Review Classify-3 | practice |
SC.6.L.15.1 Analyze and describe how and why organisms are classified according to shared characteristics with emphasis on the Linnaean system combined with the concept of Domains.
| Scientific Names | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Classify-2 | practice |
| Review Classify-1 | practice |
| Review Classify-3 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.V.3.b Use a simple classification system to classify unfamiliar Utah plants or animals (e.g., fish/amphibians/reptile/bird/mammal, invertebrate/vertebrate, tree/shrub/grass, deciduous/conifers).
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Scientific Names | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Classify-2 | practice |
| Review Classify-1 | practice |
| Review Classify-3 | practice |
UT.7.V.2.c Generalize rules for classification.
| Scientific Names | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Classify-2 | practice |
| Review Classify-1 | practice |
| Review Classify-3 | practice |
NGSS
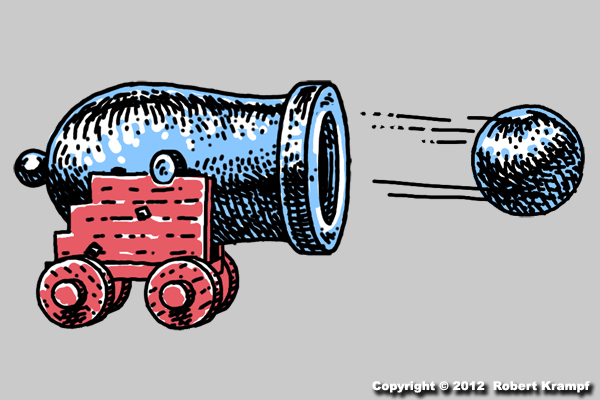
When this cannon fires, cannon and the cannon ball both move, but the cannon ball moves much farther and faster than the cannon. Why?
-
The cannon ball is smaller.
No. While smaller size means a little less air resistance, that is not enough to cause the difference. -
The wheels on the cannon are stuck.
No. Even with the wheels moving freely, the cannon ball will still move much faster and much farther. -
The cannon ball is round.
No. While the round shape means a little less air resistance, that is not enough to cause the difference. -
The cannon ball weighs less.
Yes! According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, the more mass an object has, the less it will be affected by a force. Newton's Third Law of Motion tells us that the cannon and the cannon ball will both be pushed by the same amount of force, but since the cannon is much heavier (more mass), it will not move as fast or as far.If the cannon was made of very light weight plastic, so that it was much ligher (less mass) than the cannon ball, then the cannon would move farther and faster.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.P.13.3 Investigate and describe that the more mass an object has, the less effect a given force will have on the object's motion.
| The Difference Between Weight and Mass | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| High Bounce | video, checked |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
Utah
UT.3.III.2.b Compare and chart the relative effects of a force of the same strength on objects of different weight (e.g., the breeze from a fan will move a piece of paper but may not move a piece of cardboard).
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| High Bounce | video, checked |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
NGSS
MS-PS2-2 Plan an investigation to provide evidence that the change in an object’s motion depends on the sum of the forces on the object and the mass of the object.
| Strange Flame, part 2 | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 1 | video, checked |
| Science Friction | video, checked |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| More Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Bernoulli Effect | video |
| The Old Tablecloth Trick | video |
| Smoke Rings | video |
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| The Difference Between Weight and Mass | video, checked |
| Torque | video |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Newton's First Law of Motion | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |

The brown spots on this fern contain spores. How are spores different from seeds?
-
Spores are much smaller, because they do not contain stored food for the young plant.
That is part of the answer. Most seeds contain stored food for the developing plant. Orchid seeds are an exception.. -
Spores are a form of asexual reproduction.
That is part of the answer. Spores contain only the genetic material from the parent plant. -
Spores develop into a different kind of plant from the parent.
This is part of the answer. Ferns have alternation of generations, which means that the spores grow into a plant called a prothallia. The prothallia produces male and female sex cells, which join, and grow into another fern plant. -
All of the above.
Yes! All three of the answers are correct.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.3.L.15.2 Classify flowering and nonflowering plants into major groups such as those that produce seeds, or those like ferns and mosses that produce spores, according to their physical characteristics.
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
SC.4.L.16.4 Compare and contrast the major stages in the life cycles of Florida plants and animals, such as those that undergo incomplete and complete metamorphosis, and flowering and nonflowering seedbearing
plants.
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Creating a Sprout Guide | text page, photography, free |
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-4 | practice |
Utah
UT.5.V.1.e Investigate variations and similarities in plants grown from seeds of a parent plant (e.g., how seeds from the same plant species can produce different colored flowers or identical flowers).
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
UT.7.IV.1.c Cite examples of organisms that reproduce sexually (e.g., rats, mosquitoes, salmon, sunflowers) and those that reproduce asexually (e.g., hydra, planaria, bacteria, fungi, cuttings from house plants).
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
NGSS
MS-LS1-4 Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful reproduction of animals and plants respectively.
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| How Does a Butterfly Fly? | text page, free |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
MS-LS3-2 Develop and use a model to describe why asexual reproduction results in offspring with identical genetic information and sexual reproduction results in offspring with genetic variation.
| Extracting Your Own DNA | video |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
MS-LS3-2 Develop and use a model to describe why asexual reproduction results in offspring with identical genetic information and sexual reproduction results in offspring with genetic variation.
| Extracting Your Own DNA | video |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |

When you break the mineral calcite, it breaks into shapes with flat, smooth sides. This is an example of:
-
Cleavage
Yes! A mineral has cleavage when it breaks to form flat, smooth surfaces. -
Fracture
No. There are different kinds of fractures, but none of them form flat, smooth surfaces. -
Conchoidal
No. A conchoidal fracture is the shell-shaped break that is commonly seen when glass breaks. A conchoidal fracture is not flat.

-
Hardness
No. Hardness tells us how easily a mineral can be scratched, not how it breaks.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.2 Identify the physical properties of common earth-forming minerals, including hardness, color, luster, cleavage, and streak color, and recognize the role of minerals in the formation of rocks.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Minerals Around You | text page, learnalong, checked |
| Review Minerals-1 | practice |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.b Observe rocks using a magnifying glass and draw shapes and colors of the minerals.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
UT.8.III.1.b Observe and describe the minerals found in rocks (e.g., shape, color, luster, texture, hardness).
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Review Minerals-1 | practice |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties.
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| Making Turmeric Paper | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Floating Bubbles | video, checked |
| Finding Fat in Foods | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Fireworks Colors | video |
| Iron Cereal | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Density: Ice, Oil, and Water | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 1 | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 2 | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| A Cool Change | text page |
| Acid Hunt | text page |
| Review Minerals-2 | practice |
| Review Minerals-3 | practice |
| Review Minerals-4 | practice |
| Review Minerals-5 | practice |
| Review Minerals-6 | practice |
| Review Minerals-7 | practice |
| Review Minerals-8 | practice |

From our new home in Utah, the stars are so bright that we can even see the Milky Way Galaxy. How far is the Milky Way Galaxy from Earth?
-
923 light years.
-
92.3 light years.
-
9.23 light years.
-
We are in the Milky Way Galaxy.
Think about it, and when you think you know the answer, then continue.
The Sun and you and me and all the stars that we can see are in the galaxy we call the Milky Way.
923 light years.
92.3 light years.
9.23 light years.
We are in the Milky Way Galaxy.
Think about it, and when you think you know the answer, then continue.
The Sun and you and me and all the stars that we can see are in the galaxy we call the Milky Way.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.E.5.1 Recognize that a galaxy consists of gas, dust, and many stars, including any objects orbiting the stars. Identify our home galaxy as the Milky Way.
| Review Space-2 | practice |
| Review Space-1 | practice |
| Review Space-10 | practice |
SC.8.E.5.1 Recognize that there are enormous distances between objects in space and apply our knowledge of light and space travel to understand this distance.
| Sunprints | video |
| Making a Scale Model of the Solar System | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Sunglass Science: Birefringence | video, free, Updated |
| Sunglass Science: Polarized Light | video, free, Updated |
| A Color You Can't See | video, free, checked |
| How Far is That Planet? | text page |
| CD Spectrum | text page |
| Review Space-1 | practice |
| Review Light-3 | practice |
Utah
UT.6.IV.1.d Compare the size of the Milky Way galaxy to the size of the known universe.
| Review Space-1 | practice |
NGSS
2-LS2-1 Plan and conduct an investigation to determine if plants need sunlight and water to grow.
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Plants-1 | practice |
